Calibrate a map
Before a map can be used in QV, it must be georeferenced or “calibrated”. This requires the identification of the map type and its reference system and the assignment of specific points to known coordinates. This is essential in order to georeference the map, i.e. to enable QV to transfer map coordinates to screen coordinates and vice versa.
So, in order to use a map in QV which is located as a bitmap on your PC harddisk (for example a scanned map), three steps are required.
1. Import the map
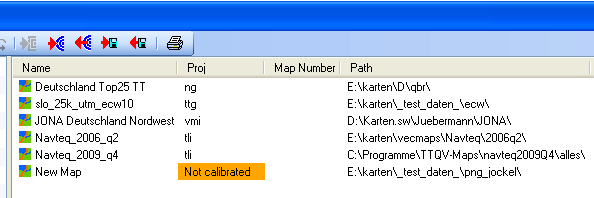
So, first of all, import the map as described in the chapter Import new map. Thereafter, you will find the map in the X-Plorer with the remark Not calibrated:
2. Open the map
In the next step, open the map in the 2D mode by clicking the icon Show in map  .
.
As the map ist still not calibrated, QV will indicate in the bottom line the positions as pixel coordinates. The coordinates of the mouse pointer ar indicated in black, those of the map cursor in magenta.
3. Calibrate the map
Open the calibrating assistant by selecting File > Calibrate map… from the main menu.
In the first page you can enter some general information like Name, Scale, Map number and additional Info.
Then, click Continue to enter the map projektion.
Specifying the projection
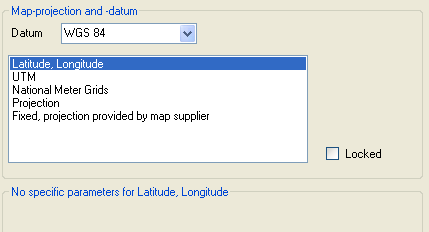
Latitudes - Longitudes
This is the simpliest mode which you should choose, if
- The exact projection of the map is unknown
- The grid of the map is only slightly curved or not curved
- The grid is labeled with longitudes and latitudes
UTM
This is the right selection for maps with a UTM grid. You will have to specify the UTM zone and the hemisphere.
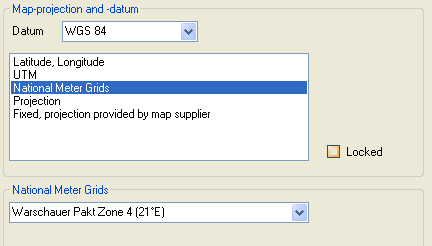
National Meter Grids
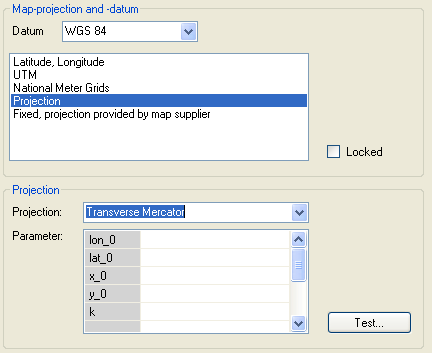
Projection
For this option you must know the exact projection of the map, including all relevant parameters.
So, choose the projection from the list and enter the required parameters into the corresponding fields.
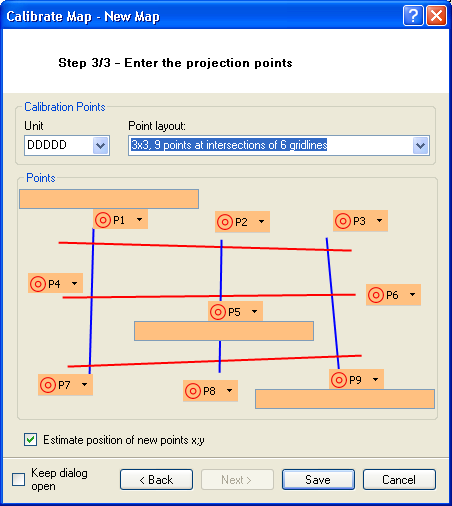
Entering the reference points
On the third page of the assistant, you will have to specify the refernece point for the calibration.
In order to make this as efficient as possible (enter as many points as necessary but not more than essential), various patterns are available.
Functions of a reference point
The status iof a reference point is indicated by colors:
To enter a point in the map, first click the corresponding button, e.g.  and the click on the corresponding point in the map. A red mark will then appear at this point of the map:
and the click on the corresponding point in the map. A red mark will then appear at this point of the map:

As confiramtion, the corresponding button in the assistant will switch to green.
Thereafter, please enter the geographic coordinate. You must enter the value in the the units which are selected under Units. Thereafter, the entry field will also switch to green.
Additionally, the Px icons have a drop-down menu: 
| Show point in map | Moves the map in order to display this point. |
| Copy geo-coordinate from a calibrated map | Using this function, you can copy the coordinate which you have to enter from a map which has already been calibrated. |
| Enter pixel coordinate manually | Through this option, you can enter the X and Y coordinates in pixel units in the corresponding box. |
| Delete point | This will delete the point definition, so that te status switches back to orange. |
Save calibration
After all points are defined, i.e. all fields indicate the status in green, click the Save button. Thereafter, the calibration will be saved, the calibration status updated in the map list and the map will be displayed. So you can control immediately, if the calibration is correct. If the software switch “Keep dialog open” is set, the assistant will not be closed, so you can make further corrections if required. Otherwise the assistant will automatically close.
Of course you can restart the assistant at any time in order to check or to modify the map calibration.
| It is important to check the calibration! Follow the latitudes and longitudes with the mouse pointer and watch the coordinates which are specified in the status line. If they are not plausible, repeat the calibration. Another test: Double click on a map point which is not close to a calibration point and save this point as a waypoint. Plot this waypoint in the map and check whether the mark is in the same place. If you have GPS tracklogs from this area, plot them in the map and check for their correct placement. |
|---|
![[Translate to English:] QuoVadis GPS](/fileadmin/_processed_/5/b/csm_QuoVadis-Logo_JTL_dadf090183.png)